(Bloomberg) — Warren Buffett is signaling wariness with the soaring stock market as the billionaire investor extends a selling streak.
Most Read from Bloomberg
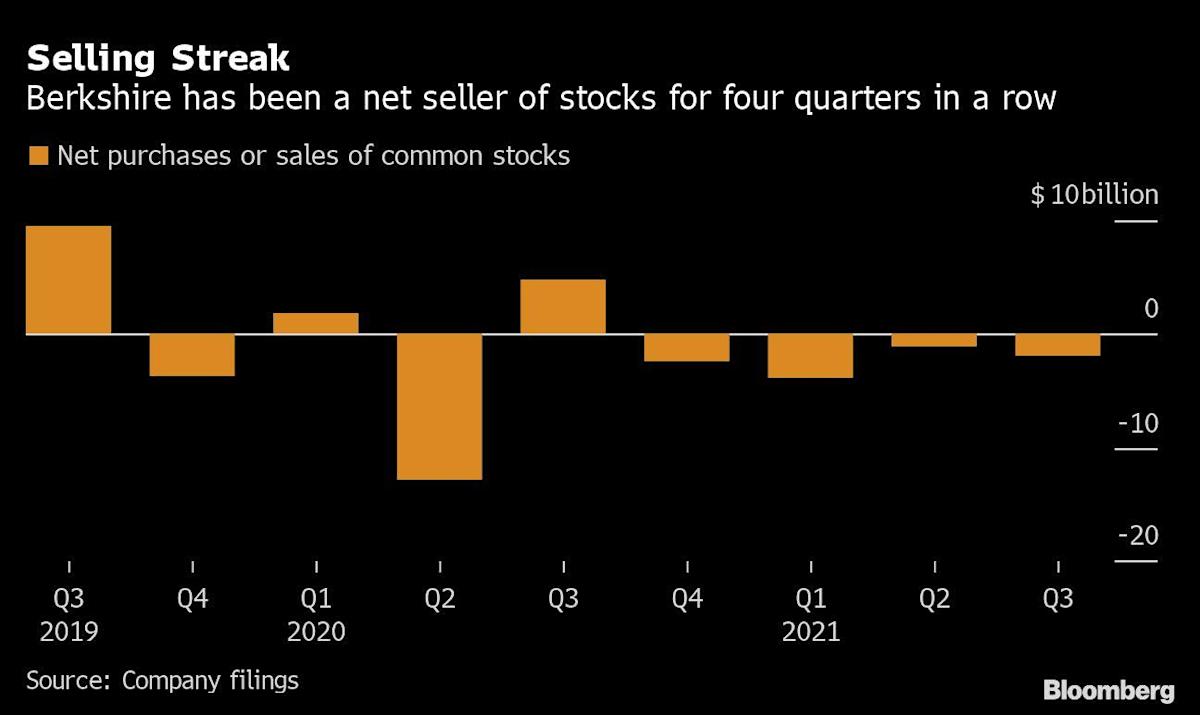
Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway Inc. was a net seller of equities for the fourth straight quarter, a trend not seen in data going back to 2008. The company ended up selling almost $2 billion more in stocks than it purchased during the period, adding to a cash pile that climbed to a record $149.2 billion.
The selling streak indicates Buffett has struggled to find bargains with the stock market hitting all-time highs. A big, splashy acquisition also eluded the conglomerate, as the 91-year old and his investing deputies confronted a combination of sky-high price tags and fierce competition from the wave of special purpose acquisition companies.
“The big issue here is that Berkshire was a net seller of stocks again this quarter,” Jim Shanahan, an analyst with Edward Jones, said in a telephone interview. “That’s the primary culprit” of the cash pile continuing to rise.
Berkshire’s sales appear to have largely come from cutting holdings in banks, insurance and financial investments, according to its third-quarter regulatory filing released Saturday. Berkshire has been paring certain stocks in recent periods, spending the second quarter trimming its investment in General Motors Co. and pulling back on some of its pharmaceutical bets. The company is set to release its third-quarter stock tweaks later this month.
While Buffett’s been a consistent net seller these past four quarters, those sales have been relatively small compared with the massive size of his stock portfolio. Over the past nine months, he’s sold almost $7 billion more of stocks than he’s bought, roughly 2.2% of the fair value of Berkshire’s stock portfolio at the end of September.
Buffett warned investors in May that Berkshire might not have much luck striking deals as SPACs gripped the market — though he also predicted the boom probably wouldn’t last. Compounding the challenge, his most recent big acquisition, the $37 billion deal for Precision Castparts five years ago, resulted in a writedown that Buffett laid squarely at his own door.
Berkshire isn’t alone in extending a cash pile amid the pandemic. Amazon.com Inc., Google-parent Alphabet Inc. and American Airlines Group Inc. were among companies that amassed significant holdings during the health crisis in a step analysts have said would likely lead to some acquisitions.
And the rising cash pile is better than the alternative in the eyes of investors including Cheviot Value Management’s Darren Pollock. Even though Buffett’s cash pile still increased to a record despite the $7.6 billion of buybacks in the third quarter, Pollock says it’s a good sign about the health of Berkshire.
“We’re happy with it because the alternative is that cash isn’t growing as much and that means that Berkshire’s operating companies aren’t of as high quality as we thought,” said Pollock, whose Cheviot owns shares in Berkshire. “To see that the cash is rising, to see that he’s deploying so much in one avenue which happens to be buybacks — it’s not acquisitions — but it’s being spent in a productive way, it’s so much better than the alternative of seeing that cash stabilize or decline without other large acquisitions.”
Here are some other key takeaways from Berkshire’s third-quarter earnings on Saturday:
Berkshire Appetite
Buffett has increasingly leaned on share buybacks as one way to deploy billions of dollars. He’s spent about $51 billion on stock buybacks since a policy tweak in 2018, outpacing the $31 billion used to purchase shares of Apple Inc., Berkshire’s largest stock bet.
In the third quarter, Berkshire bought back $7.6 billion of stock, surpassing the $6 billion of shares repurchased in the previous period.
BNSF’s Record
Record profit at Berkshire’s railroad, BNSF, and strong earnings from its energy businesses helped raise operating profit by 18% at the conglomerate during the third quarter.
That also aided in offsetting a painful quarter for Berkshire’s insurers. Those businesses reported an underwriting loss that widened to $784 million amid heightened catastrophe costs and worsening claims trends at auto insurer Geico.
Most Read from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.