It feels like forever since we all were able to look back on the last 12 months and not say “good riddance, you garbage fire hellscape of a year.” 2021 kicked off with riots at the Capitol and though things seemed to quiet down a little after, all was not well in tech.
There are companies that are obvious additions to this list, like Meta (formerly Facebook) with its repeated transgressions this year. Activision Blizzard faces multiple lawsuits and investigations over allegations of sexual harassment and gender discrimination in the workplace, revealing that despite all the growth we hoped we’d made in the last few years, the gaming industry remains toxic.
But there are other businesses that made the lives of workers and consumers miserable on a daily basis, too. And all major companies in Big Tech have to share in the blame. When we put together this roundup of the worst players in tech this year, it’s clear that we’re overdue a reckoning. Let’s hope that in the years to come, the people with the most influence learn how to treat people better.

Carlos Barria / reuters
For the company now known as Meta, 2021 went sideways from the very beginning.
For all its talk about safeguarding the 2020 presidential election, Facebook was ill-prepared for the insurrection that followed on January 6th. The company failed to recognize the danger posed by the “Stop the Steal” movement until after a violent mob stormed the Capitol. Then COO Sheryl Sandberg downplayed the role Facebook had played in the insurrection, only to be promptly proven wrong. In the end, the events of January 6th ultimately forced the platform to do something it had studiously avoided for most of the Trump presidency: Enforce its rules for his account. (Sort of. Trump’s Facebook ban isn’t permanent.)
Elsewhere, the arrival of coronavirus vaccines only highlighted Facebook’s poor track record at combating vaccine misinformation, which surged throughout the pandemic. After years of dragging its feet, the company finally banned misleading or inaccurate vaccine content. But enough damage had already been done. The US Surgeon General said viral health misinformation was an “urgent threat” to public health. President Joe Biden went a step further: saying that Facebook was “killing people.”
This year was also the first time the Oversight Board, created so Facebook could outsource its thorny content moderation decisions, was operational. The body has pushed the social network to change some policies and has repeatedly criticized the company for a lack of transparency and ability to enforce its rules evenly.
POOL New / reuters
Then came Frances Haugen, the former employee turned whistleblower who left the company with thousands of pages of internal research and other documents that have since become known as the “Facebook Papers.” Her disclosures paint a picture of a company that is unwilling or unable to adequately tackle some of its biggest problems, particularly outside the United States and Europe. She also revealed internal research about the effect of Instagram on teens, which was immediately seized on by lawmakers in Congress.
Amid all that, Zuckerberg announced not an overhaul of the company’s policies, nor a review of its internal research, but… a new name: Meta. It’s meant to symbolize the company’s newfound commitment to a metaverse that no one can fully explain. Will the company change its content moderation policies when it comes to the metaverse? Will it invest more in safety for non-western countries? How will it address hate speech in the metaverse? Facebook, er Meta, has yet to meaningfully address any of those questions. But if recent history is a guide, we all have a lot to worry about.
— Karissa Bell
Truth Social
You’d be forgiven if, amidst the news of actual importance in 2021, you forgot about TRUTH Social — the upcoming site built by disgraced former president Donald J. Trump. Trump spent most of his presidency fear-mongering and spouting lies on Twitter and other social platforms, which finally resulted in him being banned from Twitter, Facebook, YouTube and most other services of note. While Trump is wrongfully convinced that this is an unlawful witch hunt, he’s also decided to say “who needs ‘em?” and launch his own.
TRUTH was announced in October, with a limited beta planned for November before a full public launch in 2022. Immediately, dedicated internet pranksters found a test version of the site in the open and signed up for a slew of high-profile accounts (including, naturally, donaldjtrump and mikepence). (The donaldjtrump account had a profile picture of a defecating pig, for good measure.)
The test was quickly shut down, but not before it was revealed to be basically a Twitter clone running on the open-source software Mastodon. But since TRUTH Social didn’t properly cite its usage and didn’t share the source code with users, the site was in violation of Mastadon’s open-source license agreement.
TRUTH’S terms of service were also revealed, and we learned that it was essentially hoping to be protected by Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, which currently states that services like Twitter and even TRUTH aren’t responsible for what their users post. This shields companies from liability for the awful things those users might share.
We blissfully haven’t heard much about TRUTH Social since its disastrous first few days in the public spotlight; the company missed the November beta launch date and there’s no update on when the promised full launch might happen. Based on these early struggles, it’s easy to call TRUTH Social a loser of 2021 – but the citizens of the internet who didn’t have to deal with the ugly reality of a Trump-backed social network are all undoubtedly winners.
— Nathan Ingraham
Wolfgang Rattay / reuters
Global chip supply
The rise in demand for PCs, gadgets and cars couldn’t keep up with the slowing production in global chip supply. That’s why it’s still tough to find a PlayStation 5 a year after its launch, and why used car prices have gone absolutely bonkers. This is our new reality for the next few years, at least until chip suppliers can ramp up production and start spinning up new fabrication plants. Basically, be prepared to use all of your gear for a bit longer without upgrading.
— Devindra Hardawar
Activision Blizzard
There are far too many stories of sexual harassment and discrimination in the video game industry. Over the past few years, reports of systemic misogyny and abuse have poured out of Riot Games, Ubisoft and many other studios large and small, and the problems date back decades.
Among all this trash, Activision Blizzard stands out as one of the worst.
Activision Blizzard was accused of fostering a culture of sexual harassment by California’s fair-employment agency in July, and multiple organizations have since launched investigations into the studio, uncovering years of mismanagement in the process. According to the California lawsuit, leaders at the studio cultivated a frat house-style environment where sexual harassment was commonplace and gender discrimination was systemic. The fair employment agency found that all of Activision Blizzard’s top leadership positions were held by white men, just 20 percent of all employees identified as women and reports of harassment were routinely ignored.
In December, an employee named Christine went public with her experience at Blizzard, saying she was inappropriately touched by male coworkers, propositioned for sex by her superiors and subjected to crude comments about her body. After reporting the abuse to management, she said she was demoted and told to “get over it.”

Allen J. Schaben via Getty Images
Activision Blizzard’s response to these accusations has been tragic. Back in July, CEO Bobby Kotick sent an email to employees dismissing the California lawsuit, but he signed a female employee’s name to it. The response was roundly and loudly criticized, with employees calling it “insulting” and “abhorrent.” Kotick let Frances Townsend, one of the few women executives at Activision Blizzard, take the heat for that letter for months, losing her spot on the studio’s women’s network in the process. Publicly, Kotick called the email “tone-deaf.”
Blizzard head J. Allen Brack lost his job shortly after the lawsuit was filed, and Kotick offered a co-leadership role to Mike Ybarra and Jennifer Oneal, who became the first woman to hold a president title since the studio’s founding in 1979. Oneal left the company shortly after this promotion, reportedly because she was being paid less than Ybarra, and she felt “tokenized, marginalized and discriminated against” at the studio.
Activision Blizzard employees have walked out multiple times this year, calling for a culture shift. Major business partners, including PlayStation and Xbox, have said they’re reevaluating their relationships with the studio. Shareholders and media outlets alike are calling for Kotick to resign.
At this point, investors, employees, analysts, major gaming companies and multiple government agencies agree that Activision Blizzard is a hotbed of discrimination and sexual harassment, and it’s in urgent need of restructuring. In his 30 years as CEO of Activision Blizzard, this is the closest Kotick has come to actually being ousted from his position of power.
From that angle, it almost feels like a good year for the company. Almost.
— Jessica Conditt

Miquel Benitez via Getty Images
5G
I’m so disappointed with 5G. If, like me, you’ve watched the networking standard since at least 2014, you’ll likely agree. The promises about downloading feature films in seconds were really mostly advantages of mmWave technology, which as of today still hasn’t broadly rolled out. The sub-6 network that’s more widely available today on carriers like T-Mobile and AT&T offer a barely noticeable speed boost, and the reported latency improvements it was supposed to bring haven’t been delivered in the real world.
Yes, the telecom industry did meet its target launch date of 2020 for an initial rollout of the new standard. But 5G is still too confusing for the average consumer. Any time a company says in a briefing that a new product is 5G-ready, a guaranteed follow-up question is “Does that mean sub-6 or mmWave?” And with the recent addition of mid-band spectrum to the mix, the layers of compatibility are only going to make things more tedious.
I’ve been more than forgiving in the last couple of years, but it’s been difficult to ignore the complete mess that is the state of 5G in the US today. Sure, we’ve had more pressing issues to deal with, but if consumers are going to embrace the new standards (and be convinced to spend money for the privilege of 5G on their devices), the industry needs to get its act together and either commit to a more coherent message or more consistent rollout.
— Cherlynn Low
Workers and big tech
For a long time, working at a tech giant like Google or Apple was an enviable position. But 2021 pulled back the curtain a bit on some of these companies, exposing deep-rooted issues with how employees are treated. While not everyone at these massive organizations may be dealing with sexual harassment or poor working conditions (to name just a few issues), the many employees speaking out across the industry are indicative of an underlying trend that need to be confronted by tech’s most powerful leaders.

Mike Blake / reuters
Amazon’s poor treatment of its warehouse workers is well-known, and reports persisted in 2021. At the same time, the company pushed back hard against unionization efforts in Alabama. While the union drive was defeated in a vote, a regional office of the National Labor Relations Board recently ordered a new election, effectively invalidating the results of the earlier one. The union had filed a formal objection right after the election, and while there’s no word on when a new election will take place, it’s clear that Amazon will be under intense scrutiny when it does. The same should hold if New York City Amazon workers hold a union vote; reports have indicated that could happen soon.
Apple workers also exposed issues within the company this year. In late August, a call went out for current and former employees to share stories of discrimination, harassment and retaliation that they had experienced. This led to the start of the #AppleToo website, where these stories are regularly published.
As Jess already explained in detail above, employees at Activision Blizzard spoke up about a misogynistic culture rife with sexual harassment, as well. Reports indicated male executives groped female colleagues while other employees joked about rape or ignored women for promotions. The revelations have been so damning a lawsuit was filed by California’s Department of Fair Employment, though somehow Activision Blizzard CEO Bobby Kotick still has his job.
Google isn’t free from sin, either – employees led a massive walkout back in 2018 around how it dealt with sexual harassment (among other concerns). It hasn’t dealt with things on the same scale as other companies this year, but Google’s recent decision that it wasn’t raising pay to match inflation has certainly rankled workers. These are just a few high-profile examples, but together they paint a dark picture of the environment at some of tech’s biggest corporations. Perhaps the only upside here is that these hopefully put pressure on those in charge to clean house and improve things as quickly as possible.
— N.I.
Oculus
Meta didn’t even give Oculus a proper funeral. Instead of a celebratory news announcement, Meta CTO Andrew Bosworth pushed out a quick post to announce that the Oculus brand was being retired. What a sad fate for a company directly tied to the rise of consumer VR. (But perhaps this was the best way for Meta to separate itself from the legacy of Oculus’s controversial founder Palmer Luckey.)
— D.H.

Joe Skipper / reuters
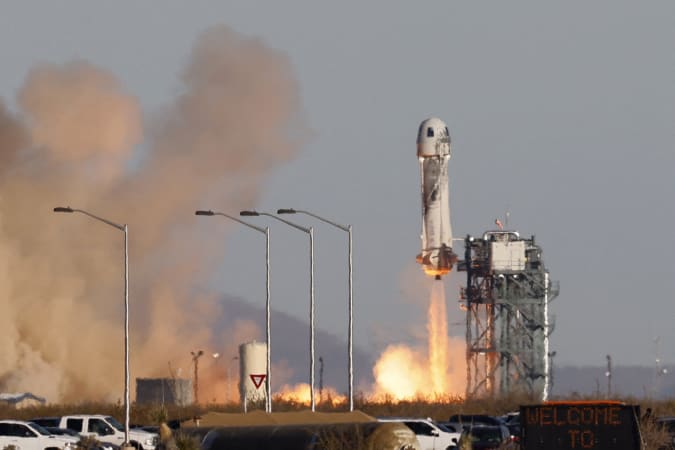
Blue Origin
2021 was a massive year for the burgeoning private spacelift industry. Firsts were made, records were achieved and billions of dollars worth of government contracts were awarded. It should have been a surefire win for all three of the industry’s leading companies — SpaceX, Virgin Galactic, and Blue Origin — but then one of them managed to repeatedly shoot itself in the proverbial landing strut more than the other two combined.
Now, that’s not to say Blue Origin didn’t enjoy its share of success this year. CEO Jeff Bezos put his money where his oversized stetson is and made a historic trip out to the Karman line along with both the oldest (at least at that point) and youngest people to ever venture into space. This past November, the company even won financial backing from NASA to help build out its bonkers Orbital Reef commercial space station design.
However, those achievements were often overshadowed by the company’s public pettiness and truculence. For example, ahead of Sir Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic making its own historic first successful flight into space this past July, Blue Origin took to Twitter to talk a little trash. This is a little rich from the company that has reportedly become a toxic workplace.
More embarrassing still was Bezos’ repeated, and ultimately unsuccessful, attempts to secure Blue Origin a lucrative NASA contract. See, back in April, NASA awarded SpaceX a $2.9 billion (yes, with a B) Artemis lunar lander contract.
Blue Origin immediately protested to the US Government Accountability Office (GAO) over NASA’s “fundamentally unfair” decision against it, bringing work on the lunar program to a standstill until July, when the GAO kindly told Blue Origin to take its $2 billion and get out. Blue Origin did not.
Instead, the space lift company doubled down, suing NASA in open federal court, “in an attempt to remedy the flaws in the acquisition process found in NASA’s Human Landing System,” per a Blue Origin representative in August. The court was not at all convinced and ruled against the plaintiffs, proving SpaceX CEO Elon Musk’s jab true. Blue Origin really can’t sue its way to the Moon.
— Andrew Tarantola
Microsoft Edge
Microsoft finally managed to make its Edge web browser a solid competitor to Chrome, Safari and Firefox by integrating the Chromium open source framework. And then, inexplicably, it began to pile on bloat, like a predatory “buy now pay later” feature and cringey anti-Chrome warnings. All of a sudden, Edge seems more like a way to trap and commodify its users, instead of delivering a solid web experience. It’s as if Microsoft made it harder to change your default browser in Windows 11 on purpose (thankfully, it’s testing out a simpler method, following plenty of industry criticism).
— D.H.
All products recommended by Engadget are selected by our editorial team, independent of our parent company. Some of our stories include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, we may earn an affiliate commission.
