If the sales field is one thing, it’s complex.
Pleasing difficult clients, stressing out over hitting goals, and mastering your company’s sales process can overwhelm just about anybody. On top of all of that, there’s a bunch of sales terminology you need to keep track of.
There are countless terms used in the sales realm, and even the experts use certain words incorrectly. Mastering every sales term is no easy feat, however, it’s necessary for communicating effectively in your sales department.
Common sales terms
Whether you’re an aspiring rep, a marketer working with your company’s sales department, or an experienced seller looking to brush up on your vocabulary, we’ve put together 81 fundamental sales terms to act as a refresher or a starting guide.
ABC
ABC is an acronym that stands for “always be closing”. This is a sales strategy that is rooted in the idea that every action a sales rep takes throughout their sales process is in pursuit of closing a deal.
Account
An account contains all the records of customer interactions, including contact information, preferred services, and transactions with your business. An account is created after the first time a customer buys from your business.
Account-based selling
Account-based selling is a strategy where the entire company coordinates to pursue high-value accounts. The departments that are most typically involved in account-based selling are sales, marketing, and customer success.
Account executive
An account executive is the person responsible for managing customer accounts. They communicate with both prospects and current customers to understand their pain points, address concerns, and close deals. An account executive needs to have extensive knowledge of the business’s value proposition so they can relate it back to the needs of a particular customer.
Account development representative
An account development representative develops sales strategies, identifies potential customers, maintains a solid understanding of the current market, and participates in any other activities that help a company meet their sales goals.
Annual contract value (ACV)
The annual contract value is the average annualized revenue per customer contract. ACV is usually compared against customer lifetime value to see how long it takes to pay back the cost of acquiring a customer.
Example: If you have a customer who signed a 4 year contract for $100,000, your ACV would be $25,000.
Business development representative (BDR)
A business development representative is a member of the sales team that focuses on outbound leads. This means they reach out to people in hopes they will become a sales opportunity.
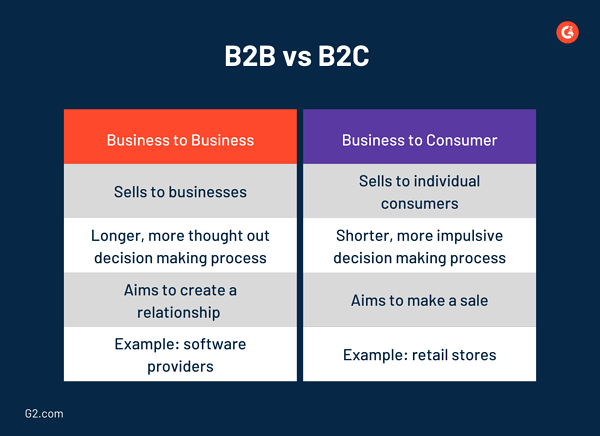
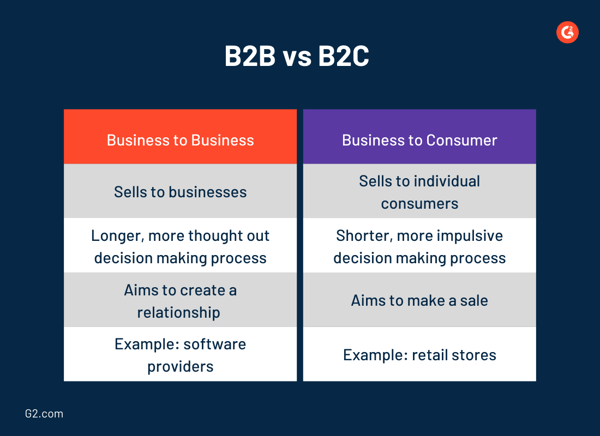
Business to business (B2B)
B2B refers to businesses that sell solutions to entire businesses.
Business to consumer (B2C)
B2C refers to businesses that sell solutions to individual consumers.
Bad leads
A bad lead is a lead that is unlikely to become a paying customer, wasting the time of a sales representative.
BANT framework
BANT is an acronym used when sales representatives are qualifying leads.
B = Budget: determines if the business has the budget to purchase the solution
A = Authority: identifies key decision-makers in the business
N = Need: verifies that the business has a real need for the solution
T = Time: checks if the business is likely to make a timely purchase
Sales representatives use BANT to help them decide whether or not a prospect is qualified, meaning they are worth pursuing.
Bottom of the funnel
The bottom of the funnel is the stage in the buying process where the customer makes a buying decision. They have moved down the sales funnel from the top (becoming aware of their problem and potential solutions), to the middle (showing interest and comparing options), to the bottom (taking action and showing loyalty to a brand).
Buyer behavior
Buyer behavior is the manner in which a customer chooses solutions. It can be influenced by their wants, needs, aspirations, occupations, and environment.
Buyer persona
A buyer persona is a representation of the ideal customer for your business. Companies create buyer personas based on market research and data about existing customers. Having a buyer persona in mind is important for marketers creating a target audience and for sales representatives qualifying leads.
Example: David is a 28-year-old architect living in Michigan who is looking for a software that will help him keep customers, accounts, and projects organized and up to date.
Buying criteria
Buying criteria is any information a customer might request so they can make a well-informed buying decision. A customer might ask about particular benefits, how your business is different/better than the competition, and how much the solution costs.
Buying process
The buying process is the stages that a buyer encounters on their journey to find a solution and buy a product. The buying process can be broken down into more specific stages, but they are all grouped into three main steps:
- Awareness: the customer identifies their problem and seeks to understand it.
- Consideration: the customer does further research to find a way to resolve their problem and considers their options.
- Decision: the customer decides on a solution.
Buying signal
A buying signal is a verbal or nonverbal cues that show a customer is ready to make a purchase, such as signing up for a free trial or asking about contract specifics. Picking up on these signals can help sales reps better focus their attention on customers that are giving off more buying signals.
Buying intent
Buying intent is the likelihood of a person making a purchase, which is realized through monitoring online buying journeys. Businesses can use tools like G2 Buyer Intent to learn the companies researching their product and find the right people to contact.
Churn rate
Churn rate is the percentage of customers that stop doing business with a company over a certain period of time. The churn rate is calculated by dividing the number of customers you lost by the number you had at the beginning of the chosen time frame.
Example: If you started your first quarter with 100 customers, and lost 8 over the course of that quarter, your churn rate would be 8%.
Closed opportunities
Closed opportunities include both closed-won and closed-lost opportunities. However, some businesses use this term to mean only closed-won opportunities.
Closed-won
Closed-won is when a sales rep closes a deal and the customer purchases a solution.
Closed-lost
Closed lost is an opportunity that does not end with a sale being made.
Closing ratio
A closing ratio is the number of deals closed compared to the number of engaged prospects. This ratio can be used to evaluate the performance of an individual sales rep and forecast sales.
EXAMPLE: If you gave 50 value demonstrations and won 5 deals, your closing ratio would be 50:5, or 10%.
Cold calling
Cold calling is making an unsolicited call in an attempt to identify prospects and talk to them about their needs and how that company’s solution can resolve them.
Commission
Commission is additional compensation that is earned based on performance. The money typically comes from a portion of the sales revenue. Any sales related position is a common commission based job, but the percentage will be different from business to business.
Example: If a salesperson made a $100,000 sale and they get 15% commission, they would earn an additional $15,000 to their salary from the sale.
Conversion
A conversion is a person that completes a desired action, such as making a purchase or subscribing to your email newsletter.
Consumer
A consumer is someone that uses a product or service. This doesn’t always mean the consumer is buying the product. If you buy a gift and give it to your friend Bob to use, Bob is the consumer.
Conversion path
A conversion path is the steps a person takes to become a lead. The stages involved typically include people interacting with a business’ content and calls-to-action.
Conversion rate
The conversion rate is the number of conversions divided by the total number of site visitors.
Example: If you had 100 site visitors and 15 of them resulted in a conversion, your conversion rate would be 15%.
Cross-selling
Cross-selling is when a sales rep finds more than one solution that will help a particular customer. This can either happen at the time of the first purchase or later on once the sales rep has created a relationship with the customer.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
Customer acquisition cost is the cost associated with getting someone to purchase your solution. CAC is a good indicator of profitability – the amount of money extracted from customers is compared to the cost of acquiring that customer.
Example: If you make a profit of $1,000 from a customer, but acquiring them cost $1,500, you might want to reprioritize.
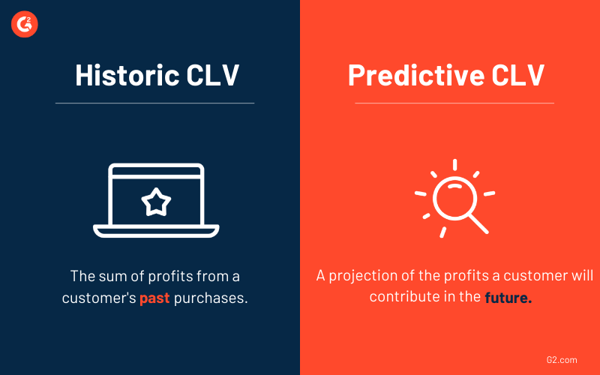
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
Customer lifetime value is a prediction of the profit that will result from a relationship with a customer. CLV can be affected by the length of the customer life cycle, retention rate, churn rate, and average profits by customer. There are two types of CLV:
Customer relationship management (CRM) systems
Customer relationship management software acts as a database full of customer information. There are three types of CRM tools:
- Operational CRM: manages day-to-day information
- Analytical CRM: analyzes customer data and behavior
- Collaborative CRM: streamlines communication with customers and makes it easy to share information across any customer-facing department
Contact information, past interactions, and previous purchases can all be found in a CRM tool. CRM is designed to help sales reps create relationships with customers and give customers a personalized experience, resulting in more sales.
Customer success
Customer success is a business practice, or department, that ensures customers achieve their desired outcome when using a business solution. This creates a mutually beneficial situation for the business and the customer – the customer resolves their pain point and the business increases the likelihood of earning that customer’s loyalty.
Decision maker
A decision maker is the person who makes the final decision of a sale. This person needs to have the authority to buy.
Demand generation
Demand generation is a marketing process that builds awareness and interest in a company’s solution. Demand generation activities include lead nurturing programs, content marketing, and search engine optimization.
Discovery call
A discovery call is the first call a sales rep makes to a prospect. This stage can also include lead qualification and determination of pain points.
Field sales rep
A field sales rep is a traveling salesperson who presents value demonstrations to potential customers. Their goal is to close and make a sale.
Forecasting
Forecasting is the act of estimating future sales so companies can make better business decisions and predict performance. Forecasts can be based on past sales data, industry comparisons, or economic trends.
Gatekeeper
A gatekeeper is a person that either enables or prevents information from reaching the intended person at a company. An example of this would be a personal assistant giving a message to a decision maker, the intended recipient.
Inside sales rep
An inside sales rep is a salesperson that conducts most of their business over the phone or online.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
A key performance indicator is a measurable value that indicates how effectively a business is reaching its goals and objectives. KPIs exist at multiple levels – a high-level KPI would focus on overall performance, such as annual growth, and a low-level KPI would focus more on day to day activities, such as sales emails sent.
Lead
A lead is a person or company that has expressed interest in another company’s solution that might eventually become a customer. Businesses can gather leads through marketing, trade shows, or networking.
Lead generation
Lead generation is the process of attracting people and converting them into prospects through activities such as website optimization, social media, and email marketing.
Lead qualification
Lead qualification is the process of determining whether or not a lead is worth pursuing. Sales reps use the BANT framework to qualify leads and draw conclusions about whether or not they have a high chance of becoming a long term customer. If a sales rep finds out that the lead doesn’t have the budget or need for the solution, they will make them a low priority.
Lead scoring
Lead scoring is a method that ranks prospects according to the value they can add to the business. The purpose of lead scoring is to help sales reps understand how they should prioritize their time and energy to make the most profit.
Mark-up
A mark-up is the amount added to the price of a solution to cover overhead.
Marketing qualified lead (MQL)
A marketing qualified lead is a lead that is qualified as interested in a business based on engagement with their marketing materials.
Middle of the funnel (MOFU)
The middle of the funnel is the part of the buying process where a lead conducts research to find a solution to the problem at hand. At this point, a lead will likely be looking at the features specific to your solution and customer reviews.
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
Monthly recurring revenue is the amount a business receives per month. This metric is usually used if the business is subscription-based.
Net promoter score
A net promoter score is a customer satisfaction metric that measures how likely a customer is to recommend your solution. This data is usually collected using a survey. Based on the rating they give, a customer is either considered a detractor (wouldn’t buy the solution again or recommend it), passive (satisfied but wouldn’t necessarily promote the solution), or a promoter (a repeat buyer that acts as a brand ambassador). Some industries use a scale of 0-10, while others use 0-100.
Objection
Objections refer to any questions or concerns from a prospect after a sales rep has performed a value demonstration. Common objections have to do with budget, authority, need, and timing (BANT). Handling these objections is a step in the sales process and a necessary skill of any sales rep.
Onboarding
Onboarding is the act of introducing your solution to a customer and getting them set up to use it after they buy. It can also refer to hiring and training a new sales rep.
Opportunity
An opportunity is a contact or prospect that has been qualified and is considered worthy of pursuing. It is important to note that the definition of an opportunity can vary across businesses. The general idea is that they show potential for becoming a customer.
Pain point
A pain point is a customer’s need. Identifying the pain points of a particular customer and showing how their solution can relieve them is necessary for sales reps trying to close a deal. Common customer pain points include spending too much on a solution, wasting time when buying, experiencing a bad selling process, and not getting enough post sale support.
Positioning statement
Positioning statements are comments or questions a sales rep uses to engage the prospect. The purpose of a positioning statement is to start a conversation with the consumer and learn about their pain points.
Profit margin
Profit margin is a ratio of profitability that reveals how much money a company actually makes. It is the amount by which revenue from sales exceeds costs. To calculate profit margin, divide your gross profit (revenue-cost of goods sold) by revenue.
Example: If your gross profit was $500, and your revenue was $2000, your profit margin would be .25, or 25%.
Prospecting
Prospecting is the process of looking for potential buyers. This is the first step in the sales process, and the goal is to move these prospects down the sales funnel and convert them into loyal customers.
Qualified lead
Qualified leads are leads that have been deemed more likely to become a customer based on certain criteria they provided or you discovered. There are two types of leads.
- Sales qualified lead: a prospective buyer that has been vetted by sales.
- Marketing qualified lead: a prospective buyer that has shown interest in a business by engaging in their web content.
Quota
A quota is a set amount of sales that a rep is expected to meet over a given time frame.
Sales development representative
A sales development representative is an inside rep that focuses on inbound leads, which are leads that approach your business and express interest in your solution.
Sales enablement
Sales enablement is a strategy that enables a sales team with the tools, processes, training, and other resources they need to improve their performance and help provide for the customer.
Sales funnel
A sales funnel is a model that outlines the customer journey in six key stages: awareness, interest, consideration, intent, evaluation, and purchase.
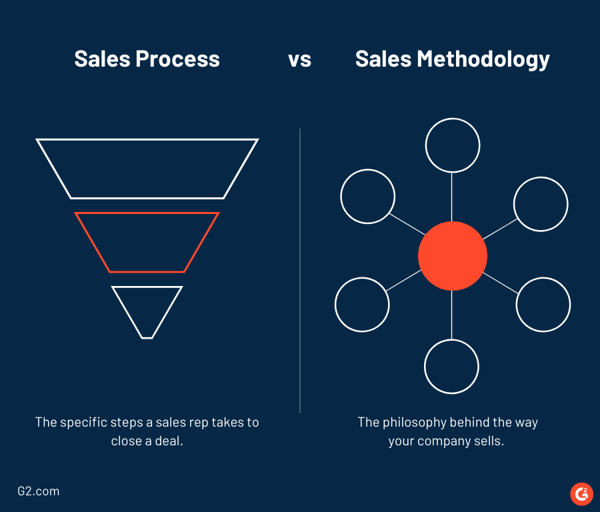
Sales methodology
A sales methodology is the framework that outlines how your sales reps approach each step in the selling process. A sales methodology includes philosophy, values, and principles.
Sales process
A sales process refers to the concrete steps and actions a sales rep goes through to make a sale. These are repeatable steps to convert a prospect into a loyal customer.
The sales process and sales methodology are often confused, so let’s break it down visually.
Sales pipeline
The sales pipeline represents a step by step process that a sales rep takes to move someone from being a prospect to a loyal customer. The pipeline is divided into stages based on the customer’s readiness to buy.
Sales pipeline coverage
Sales pipeline coverage is a ratio that compares how full your sales pipeline is against your quota in a given period. It acts as a good indicator of sales team performance and helps forecast your company’s ability to grow.
Service level agreement
A service level agreement is an agreement between the sales and marketing departments of a business that defines their expectations for each other. The service level agreement exists to make sure the sales and marketing departments are aligned and complement each other’s work.
Smarketing
Smarketing refers to aligned sales and marketing efforts. The word sounds silly, but the principle behind it is crucial for the success of a business. Marketing and sales need to support each other, and that requires a lot of communication and collaboration.
Social selling
Social selling is the act of using social media to interact with prospects. Oftentimes, this includes providing answers to simple questions that will help the prospect better understand their pain points and potential solutions.
Sound bite
A sound bite is a series of words or phrases that a sales rep has prepared to help them quickly and effectively communicate with a prospect.
Top of the funnel
The top of the funnel refers to the first stage in the buyer’s journey. At this point, buyers are still trying to understand their problems. On the selling side, it’s the job of marketers to provide content that will help educate the buyer about their problem and point out possible solutions.
Upselling
Upselling occurs when a seller finds a higher-end solution to provide an existing customer. An example of this would be when you buy a subscription to a software tool, and the next month the sales rep attempts to upsell by showing you the ropes of a more expensive version with better features.
Value proposition
A value proposition is the presentation of the benefit(s) that a solution provides to its customers. A good value proposition (that is presented during the value demonstration stage in the sales process) will cater to the individual needs of that particular customer.
Weighted sales pipeline
A weighted sales pipeline is a version of the sales pipeline where a value is placed on each opportunity based on their current stage in the sales process.
CRM terms
A significant part of understanding the basics of sales is grasping customer relationship management (CRM) software. CRM is the primary tool used by businesses to track prospect interactions and deal progress. It aids in drawing conclusions in regards to finding the most effective methods to attract, convert, and retain customers.
You’ll find that a lot of the CRM terms listed below refer to the management of a related sales term mentioned above, especially when referring to a stage in the buying process or sales funnel. This is because CRM is a system for sales reps, marketers, and customer service agents to find ways to better manage the customers in each one of these stages or their overall sales process.
Ad hoc reporting
Ad hoc reporting refers to the business intelligence process that creates reports with real-time data sets as needed by users. These reports are put together to answer a specific question in response to a particular event. Essentially ad hoc reporting shows the after effects of a certain business action.
Business intelligence
Business intelligence refers to a wide range of tools used to transform data into actions for companies to take in regards to their overall business goals, strategies, and tactics. This process uses data analytics to examine information and present relevant findings in the form of reports, dashboards, or other types of data visualization.
Cases
A case refers to an issue that a customer has presented to a sales rep that needs to be addressed. These cases can be opened for a variety of reasons, such as needing support on using a product or making changes to information in a customer’s profile.
Cloud based CRM
A cloud based CRM is CRM software that is hosted on the cloud. This means that all of the information stored on a CRM can be accessed by authenticated users on the internet, as opposed to a physical piece of hardware.
CPQ software
CPQ software, also known as configure price quote software, helps businesses automate the process of quoting and sending proposals to customers. This cycle starts when a customer expresses their needs to a business and ends when a quote is sent over. The purpose of using CPQ software is to accelerate the process, produce an accurate quote, and improve customer relations.
Contract management
Contract management refers to the process of governing the life cycles of contracts with customers, vendors, partners, and employees. Contract management begins when a contract is drawn up, and ends when it expires. However, within that time frame, the contract might be renewed or the terms may change, requiring management.
CRM analytics
CRM analytics is the analysis of data held within your business’ CRM tool. Insights gathered from the results are specific to customers and your sales pipeline, such as buying trends and areas of improvement within the sales process.
Escalations
An escalation occurs when a customer issue is directed to a higher-up department so it can be resolved more effectively. It’s possible that an issue will be presented to a department that doesn’t have the appropriate knowledge, resources, or power to resolve it. This is where escalations happen.
Lead management
Lead management refers to the process of generating, tracking, and prioritizing potential customers. Once these leads are generated from other marketing or sales actions and qualified as worthy of pursuing, they are arranged and approached based on their likelihood of making a purchase. After that initial contact is made, they are nurtured and hopefully converted into customers. This whole process is referred to as lead management.
On-premise CRM
On-premise CRM is software hosted on the company’s own server. This version of CRM is often accompanied with access to the source code, so it can be customized to fit the needs of that particular company. It also gives businesses complete control over the data being held within the CRM.
Opportunity management
Opportunity management refers to the administration of deals within a business’ sales pipeline. The purpose of this added layer of attention to opportunities is to enable sales reps to easily and conveniently close as many deals as possible.
Pipeline management
Pipeline management works to streamline every stage of the sales process and customer journey. It refers to the process of moving leads further down the pipeline, with the ultimate goal of converting them into customers.
Sales dashboard
A sales dashboard is a method of data visualization that portrays your most important sales metrics in a way that is easy to understand. Sales dashboards can be created for a variety of sales department matters, such as performance, conversions, and activities completed.
Sales performance management
Sales performance management refers to the organization of sales processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness. Areas of sales performance management include compensation plans, quota setting, and territory management.
Sales wordsmith
Not knowing the proper definition for sales terms can cause confusion, miscommunication, and misinformation being shared. Getting a firm grasp on these terms is crucial to becoming an effective and well-informed sales team member.
Looking to social proof your software sales? G2’s Seller Solution is the perfect opportunity to help build trust and credibility amongst even your most fickle prospects. Learn more today!