A voltage regulator is a circuit that creates and maintains a fixed output voltage, irrespective of changes to the input voltage or load conditions.
Types of Voltage Regulators: Linear vs Switching regulator.
Regulators are divided mainly into two parts: Linear Regulators and Switching regulators. The main point which differentiates the two types from each other is their efficiency. Linear regulators tend to have much less efficiency and are much simpler in design as compared to switching regulators. The difference between the two exists because the switching regulator converts nearly all input power to output while linear regulators dissipate power in form of heat.
Linear Voltage Regulators:-Linear regulators are step-down converters, so by definition, the output voltage is always below the input voltage. However, these regulators offer a few advantages: they are generally easy to design, dependable, cost-efficient, and offer low noise as well as a low output voltage ripple.
The examples of linear voltage regulators are as follows:-
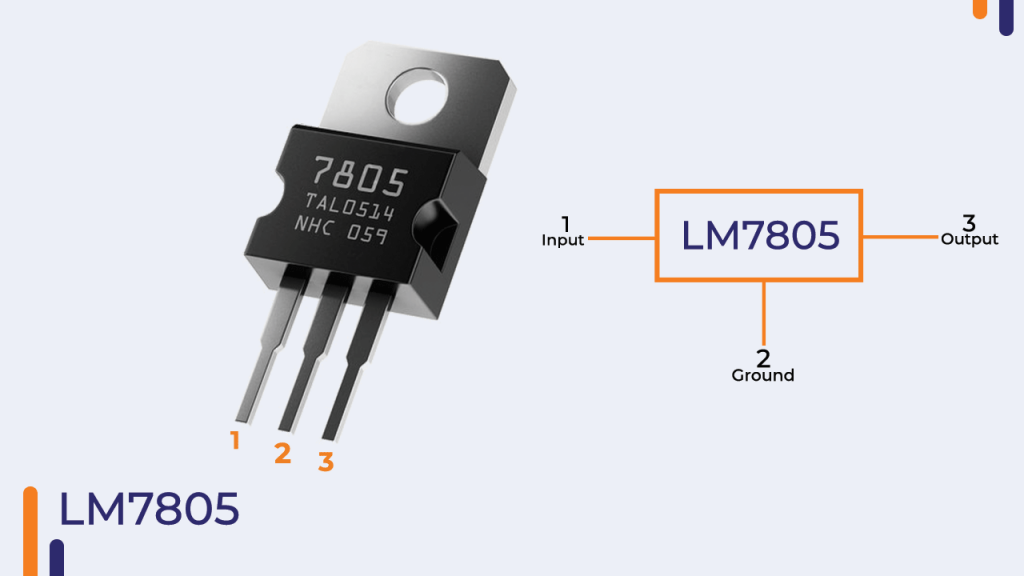
1)7805:-7805 is a three-terminal linear voltage regulator IC with a fixed output voltage of 5V which is useful in a wide range of applications. Currently, the 7805 Voltage Regulator IC is manufactured by Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, STMicroelectronics, Diodes incorporated, Infineon Technologies, etc.
As mentioned earlier, 7805 is a three-terminal device with the three pins being
A. INPUT
B. GROUND and
C. OUT


2) LM317:-It is a three-terminal-adjustable-voltage regulator and is easy to use because to set the output voltage requires only two external resistors in the LM317 voltage regulator circuit.
The three terminals are the input pin, output pin, and adjustment pin.


Switching Regulators:-Switching regulators, on the other hand, such as buck (step-down), Boost (step-up), and buck-boost (step-up/step-down), require a few more components as well as increased complexity of how various components will affect the output. Switching regulators are far more efficient in terms of power conversion where efficiency plays a big role, but linear regulators work very well as voltage regulators in low-voltage applications.
1.Buck Converter:- A Buck converter steps down a DC voltage from the input to the output. By doing so it increases the current rating of the output. A buck or step-down converter is a DC/DC switch mode power supply that is intended to buck (or lower) the input voltage of an unregulated DC supply to a stabilized lower output voltage. Buck converters are, especially compared to traditional voltage regulators, widely valued for their extremely high efficiencies which can easily exceed 95%.


2. Boost Converter:- A boost converter is a DC/DC switch-mode power supply that is intended to boost (or increase) the input voltage of an unregulated DC supply to a stabilized higher output voltage. Similar to a buck converter, a boost converter relies on an inductor, diode, capacitor, and power switch to regulate the output voltage, but they are arranged differently.


3. Buck-Boost Converter:-A buck-boost boost converter can supply a regulated DC output from a power source delivering a voltage either below or above the regulated output voltage. A buck-boost converter circuit combines elements of both a buck converter and a boost converter. however, they are often larger in footprint than either alternative.
For more info, you can watch our video.
Thank you for reading the blog.
Stay safe. Stay tuned.